What is biofuel made of?
A
biofuel is a fuel that is produced through contemporary processes from biomass,
rather than a fuel produced by the very slow geological processes involved in
the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. Since biomass technically can be
used as a fuel directly (e.g. wood logs), some people use the terms biomass and
biofuel interchangeably. More often than not, however, the word biomass simply
denotes the biological raw material the fuel is made of, or some form of
thermally/chemically altered solid end product, like torrefied pellets or
briquettes. The word biofuel is usually reserved for liquid or gaseous fuels,
used for transportation. The EIA (U.S. Energy Information Administration) follows
this naming practice. If the biomass used in the production of biofuel can
regrow quickly, the fuel is generally considered to be a form of renewable
energy
Download Sample Copy of Research
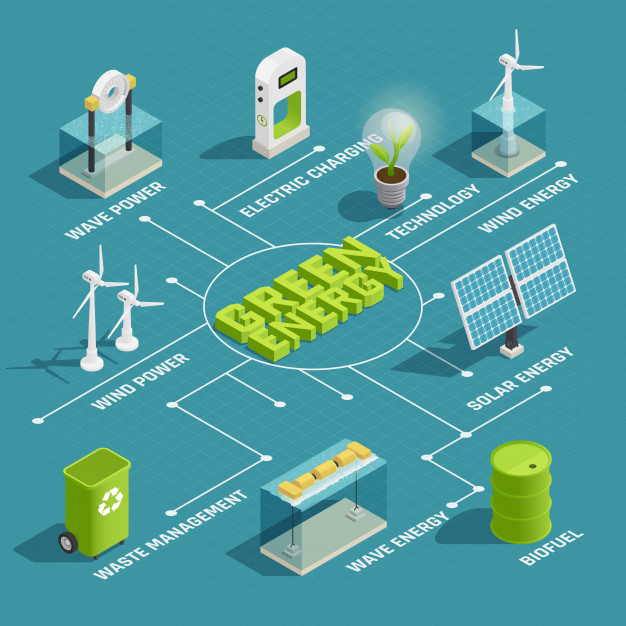
Biofuels
can be produced from plants (i.e. energy crops), or from agricultural,
commercial, domestic, and/or industrial wastes (if the waste has a biological
origin). Renewable biofuels generally involve contemporary carbon fixation,
such as those that occur in plants or microalgae through the process of
photosynthesis
Biofuels
additives are specialty chemicals that are used to enhance biofuel properties,
improve engine performance, and reduce brake specific fuel consumption (BSFC).
They play a crucial role in meeting international fuel standards. Biofuel
additives such as ethanol, diethyl ether, n-butanol, and methanol are commonly
used as biodiesel additives due to their high oxygen content. Biofuel additives
in biodiesel blends have been found to improve combustion characteristics and
combustion stability. The addition of anti-oxidant additives has also been
responsible for the reduction in NOX emissions.

Comments
Post a Comment